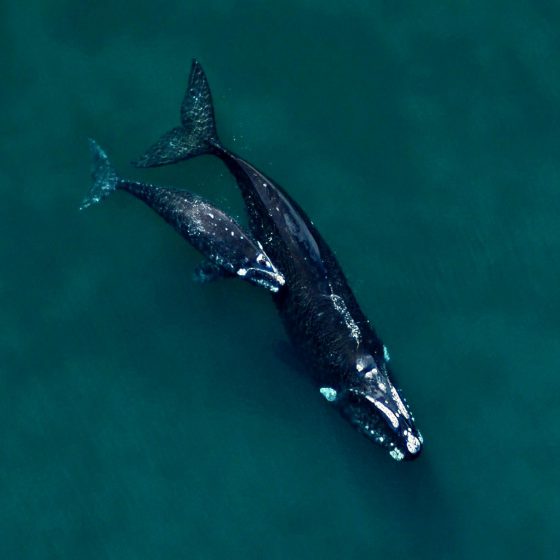
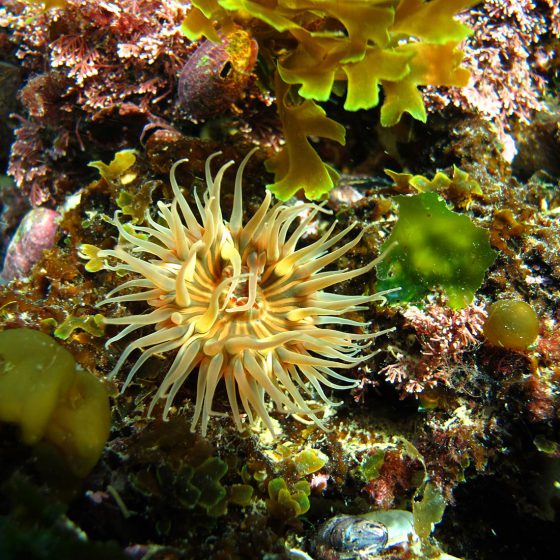
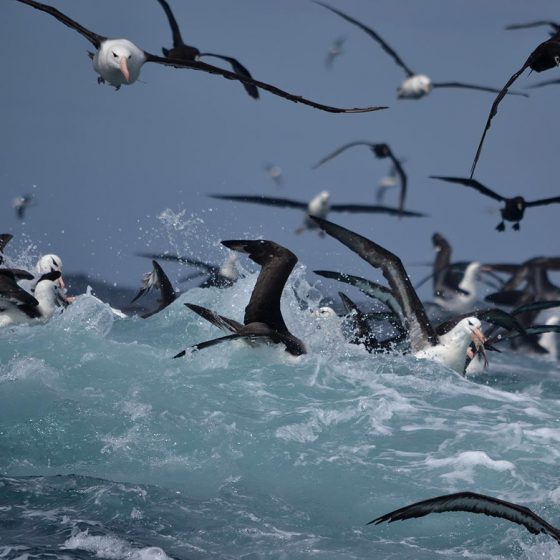
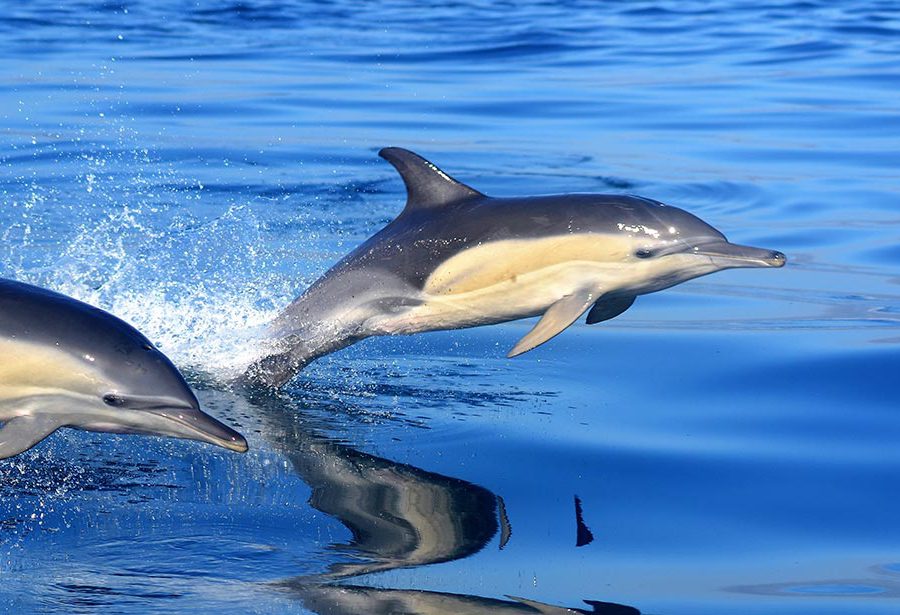
THE PATAGONIAN SEA AND AREA OF INFLUENCE
The integration of scientific, cultural, ethical, aesthetic, as well as economic values is necessary for a management that sets priority on the conservation of the diversity of species and habitats, as a basic condition for the sustainable use of resources.
© J. Vessey
We identify the “Patagonian Sea and Areas of Influence” as the area circumventing the Southern Cone of South America, that includes the waters of the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. The flow of waters resulting from tides and marine currents such as the Falklands (Malvinas), Brazilian and Cape Horn currents connects areas that are far apart, transporting living organisms. The Patagonian Sea with its areas of influence expands from southern Brazil to Tierra del Fuego in the Atlantic, whereas in the Pacific it includes the channels and fjords in southern Chile.
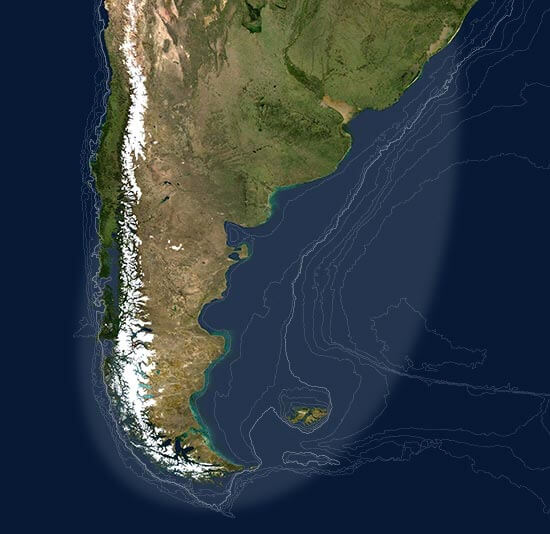

Towards the East Atlantic, the continental shelf consists of an extensive shelf and an abrupt break, the slope.
Towards the West Pacific, it is a coast that dismembers in countless islands, generating a diversity of marine environments in fjords and bays.
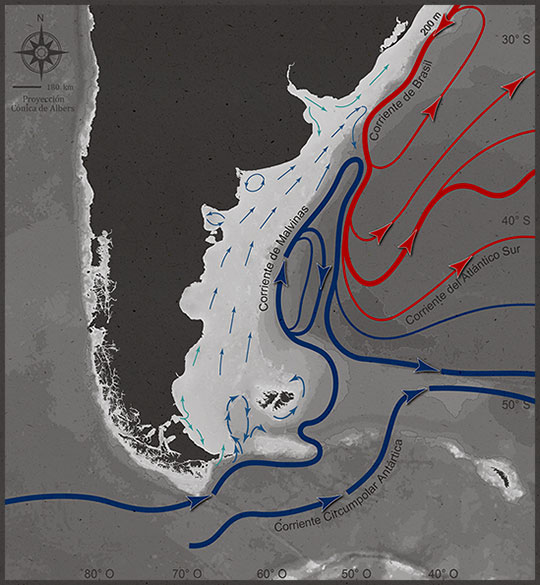
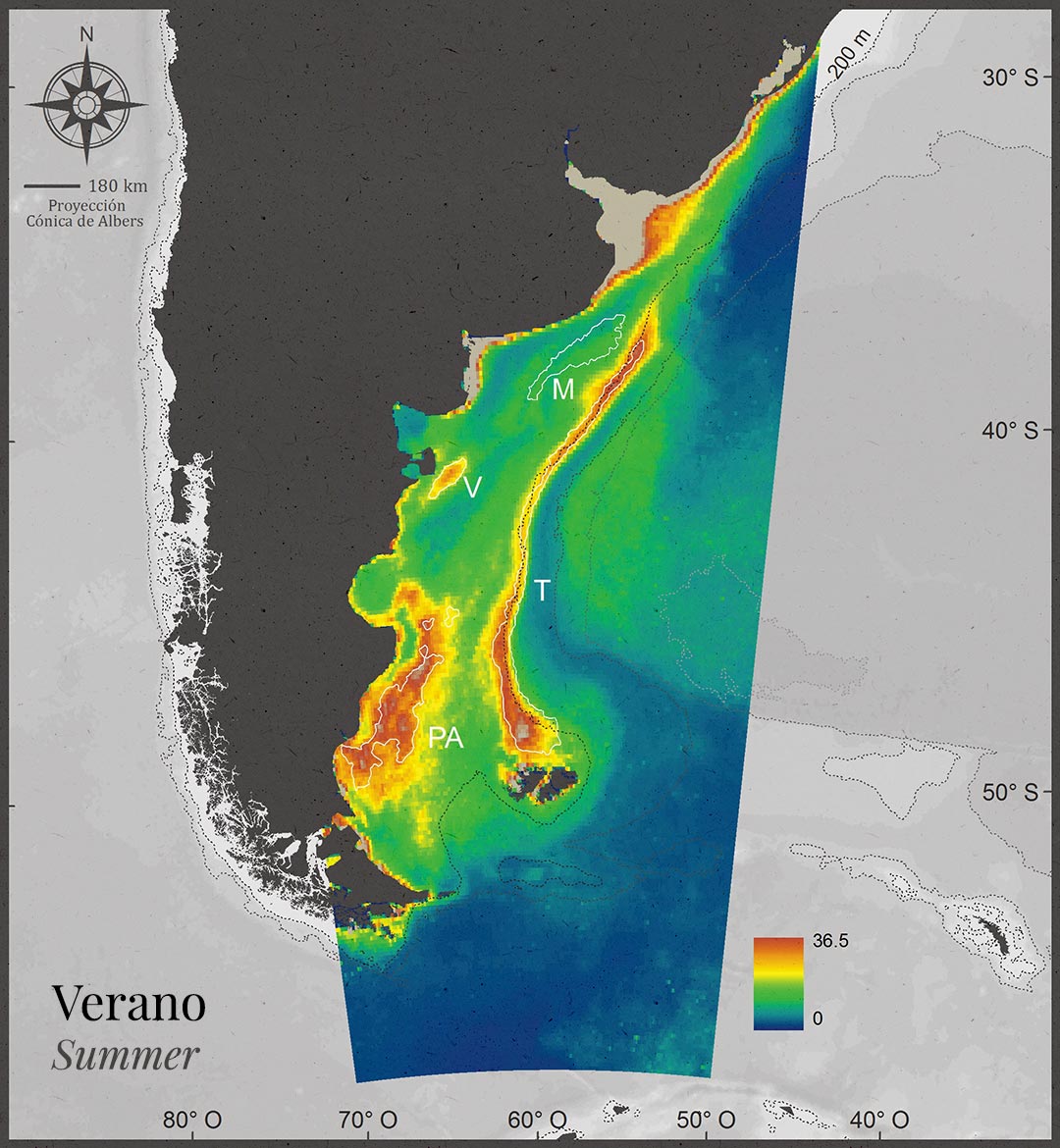
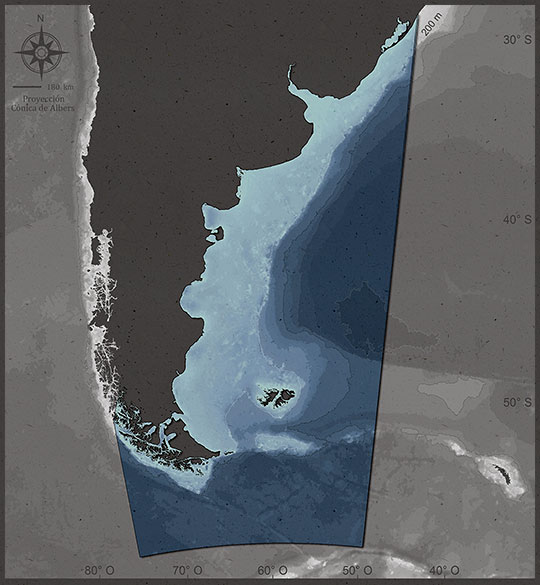
The cold current of Falklands (Malvinas) dominates the ecosystem and is a key source of productivity for the Southern Cone ocean system.
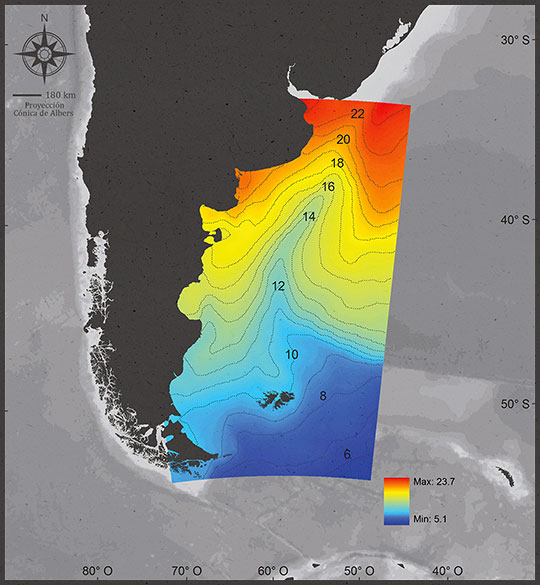
The sea surface temperature varies cyclically depending on solar radiation, cloudiness, winds and currents.
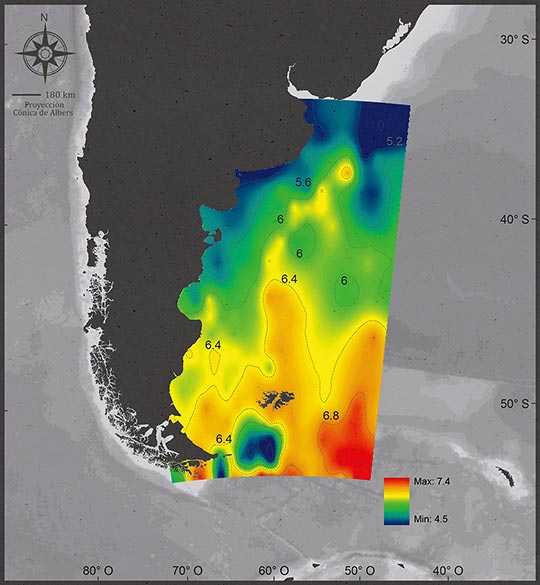
There is a high concentration of oxygen in the cold waters of the Falklands (Malvinas) current.
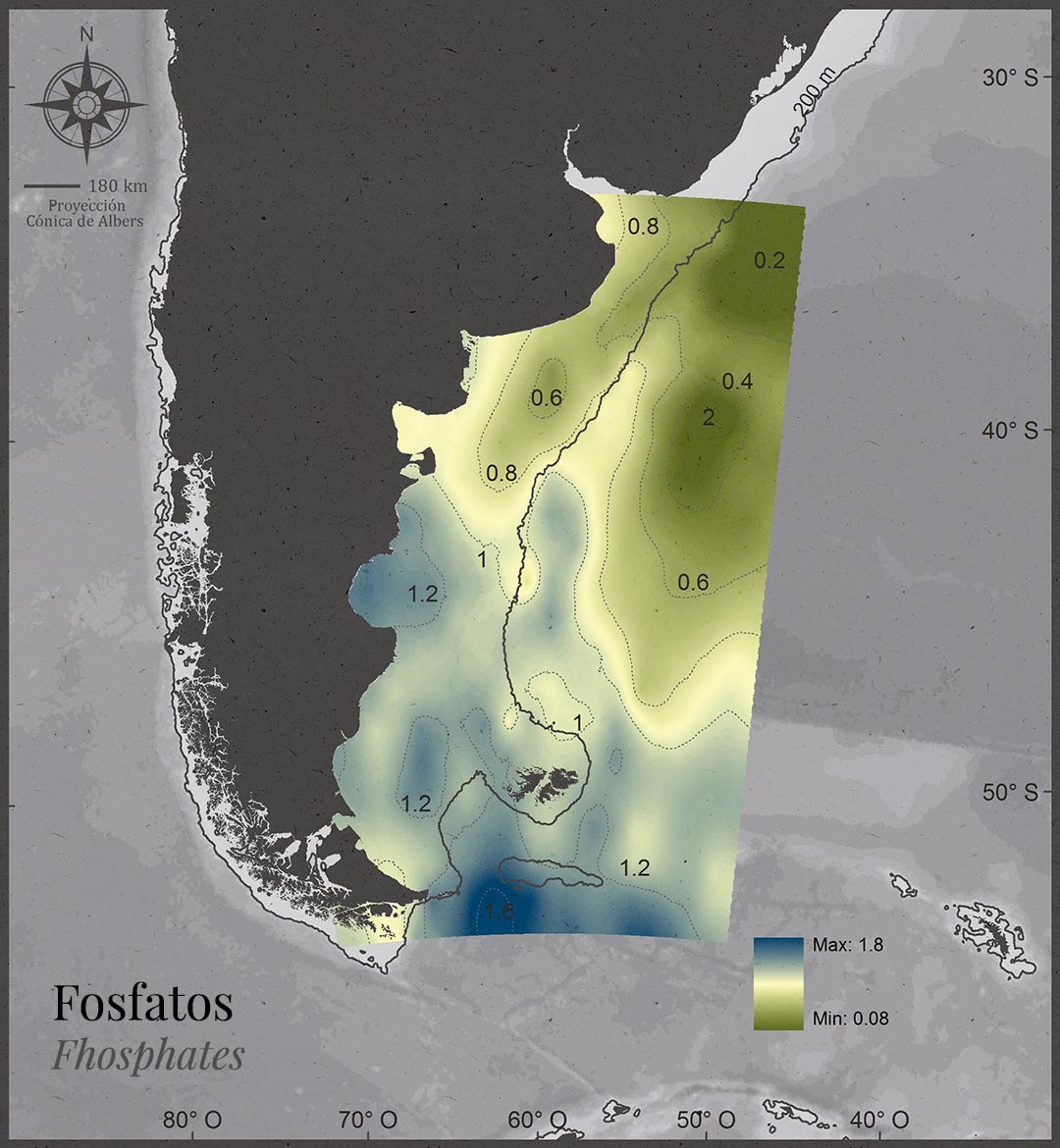
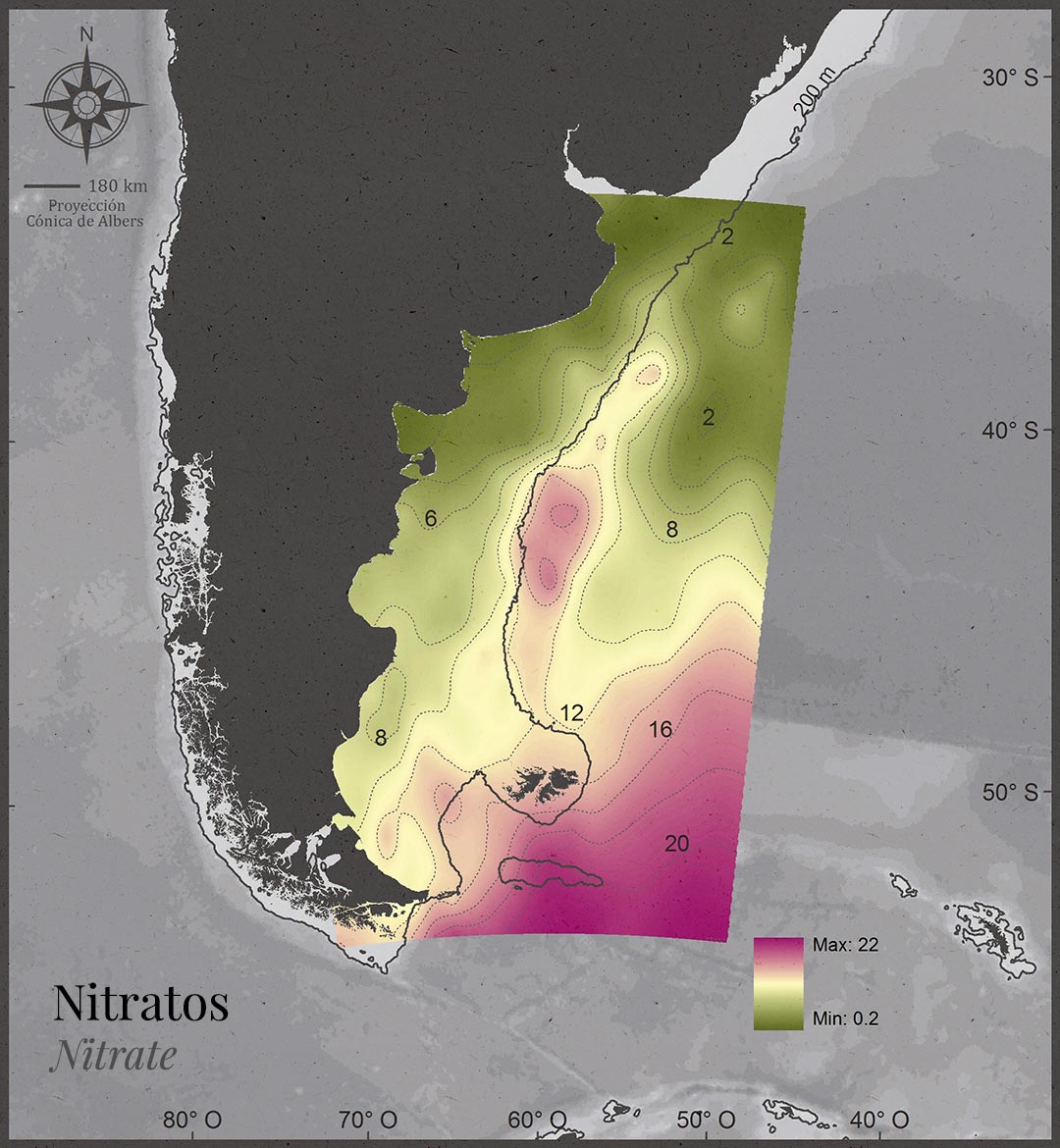
Sub-Antarctic waters are the main source of nutrients for the Patagonian Sea.
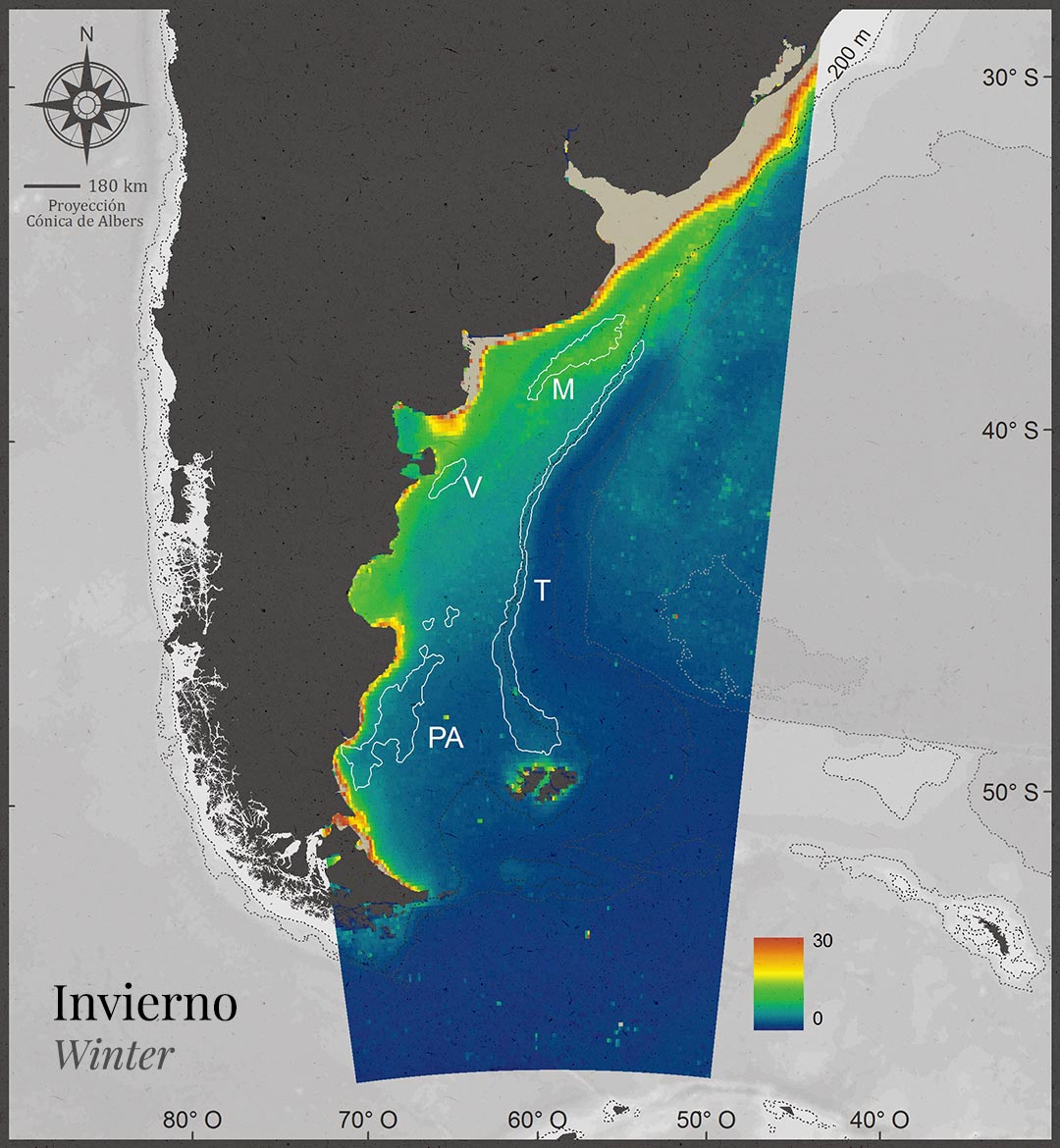
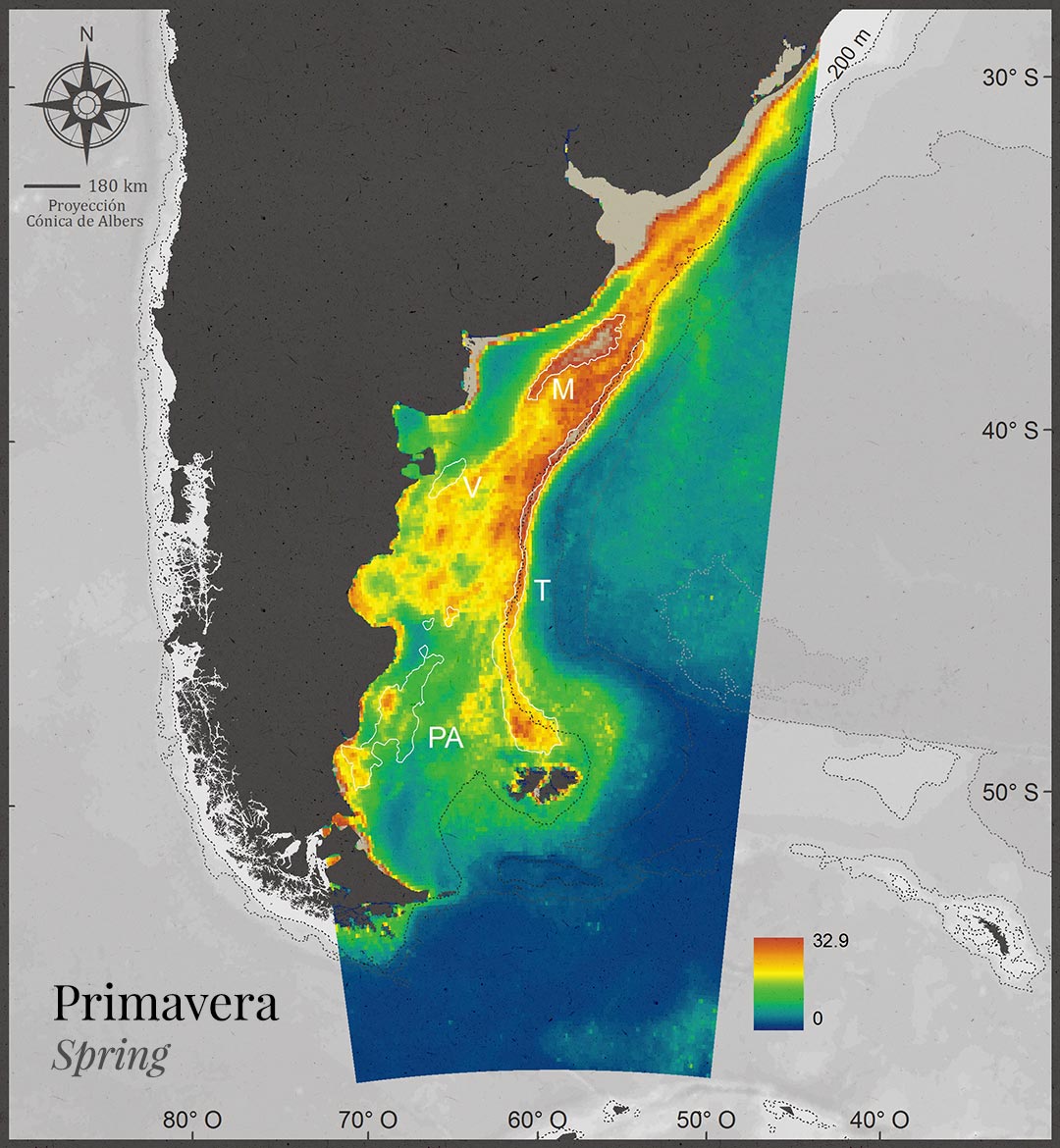
Productive chlorophyll areas are seasonally variable, but predictable in time and stable in regions.
This enormous ecosystem of at least
Includes coastal environments, islands, submarine plains, submerged slopes and deep abysses in the seabed surface.
Consists of large scale and productive oceanic areas. Includes important fisheries as well as foraging and migration areas for turtles, seabirds and marine mammals.
Politically, it includes provincial jurisdictions, exclusive economic zones of various countries, and international waters or high seas.
The reason is that the oceanographic and ecological processes of these seas take place over very vast areas. As marine currents and fauna drift beyond political boundaries with the tide and marine currents, like the Falkland (Malvinas), Brazil and Cape Horn currents, in order to promote the conservation of this ocean area, we must focus on a large scale, and encourage cooperation between countries, organizations, scientists and authorities.
“Libertad, vida, emoción, y paz. Así como preocupación y ocupación por cómo cuidarlo” (Freedom, life, emotion and peace. As well as concern and dedication to seek how to take care of it)
“Mar es conexión” (Sea is connection)
“Amor, misterio, inspiración, búsqueda” (Love, mystery, inspiration, search)
“Pasado y futuro común” (Past and common future)
“Lo impensable” (The Unthinkable)